Type 2 Diabetes: A Comprehensive Guide
Type 2 diabetes is a chronic metabolic disorder characterized by high blood sugar levels, insulin resistance, and impaired insulin secretion. It is the most common form of diabetes, accounting for approximately 90% of all diabetes cases. In this article, we will discuss the causes, symptoms, diagnosis, treatment, and management of type 2 diabetes.

Causes of Type 2 Diabetes
The exact causes of type 2 diabetes are still not fully understood, but research suggests that it is a complex interplay of genetic, environmental, and lifestyle factors. Some of the known risk factors for developing type 2 diabetes include:
1. Genetics: Having a family history of type 2 diabetes increases the risk of developing the disease.
2. Obesity: Being overweight or obese is a major risk factor for developing type 2 diabetes.
3. Physical inactivity: A sedentary lifestyle can increase the risk of developing type 2 diabetes.
4. Diet: Consuming a diet high in sugar, salt, and unhealthy fats can increase the risk of developing type 2 diabetes.
5. Age: The risk of developing type 2 diabetes increases with age, especially after the age of 45.
6. Ethnicity: Certain ethnic groups, such as African Americans, Hispanics/Latinos, and American Indians, are at higher risk of developing type 2 diabetes.
Symptoms of Type 2 Diabetes
The symptoms of type 2 diabetes can develop gradually over time, and may not be immediately noticeable. Some of the common symptoms of type 2 diabetes include:
1. Increased thirst and urination: High blood sugar levels can cause the body to produce more urine, leading to dehydration and increased thirst.
2. Fatigue: High blood sugar levels can cause fatigue, weakness, and a general feeling of being unwell.
3. Blurred vision: High blood sugar levels can cause the lens in the eye to swell, leading to blurred vision.
4. Slow healing of cuts and wounds: High blood sugar levels can impair the body’s ability to heal wounds and cuts.
5. Tingling or numbness in the hands and feet: High blood sugar levels can damage the nerves, leading to tingling or numbness in the hands and feet.
Diagnosis of Type 2 Diabetes
The diagnosis of type 2 diabetes is typically made based on a combination of clinical symptoms, physical examination, and laboratory tests. Some of the common diagnostic tests used to diagnose type 2 diabetes include:
1. Fasting blood glucose test: This test measures the level of glucose in the blood after an overnight fast.
2. Oral glucose tolerance test: This test measures the level of glucose in the blood after consuming a sugary drink.
3. Hemoglobin A1c (HbA1c) test: This test measures the average level of glucose in the blood over the past 2-3 months.
4. Random blood glucose test: This test measures the level of glucose in the blood at any given time.
Treatment and Management of Type 2 Diabetes
The treatment and management of type 2 diabetes typically involves a combination of lifestyle modifications, medications, and regular monitoring of blood sugar levels. Some of the common treatment options for type 2 diabetes include:
1. Lifestyle modifications: Maintaining a healthy diet, engaging in regular physical activity, and managing stress can all help to manage type 2 diabetes.
2. Medications: A range of medications, including metformin, sulfonylureas, and insulin, may be prescribed to help manage type 2 diabetes.
3. Insulin therapy: Insulin therapy may be necessary for some individuals with type 2 diabetes, especially if they are unable to manage their blood sugar levels with lifestyle modifications and medications.
4. Bariatric surgery: Bariatric surgery may be recommended for some individuals with type 2 diabetes, especially if they are obese and have not been able to manage their blood sugar levels with lifestyle modifications and medications.
Complications of Type 2 Diabetes
If left unmanaged, type 2 diabetes can lead to a range of complications, including:
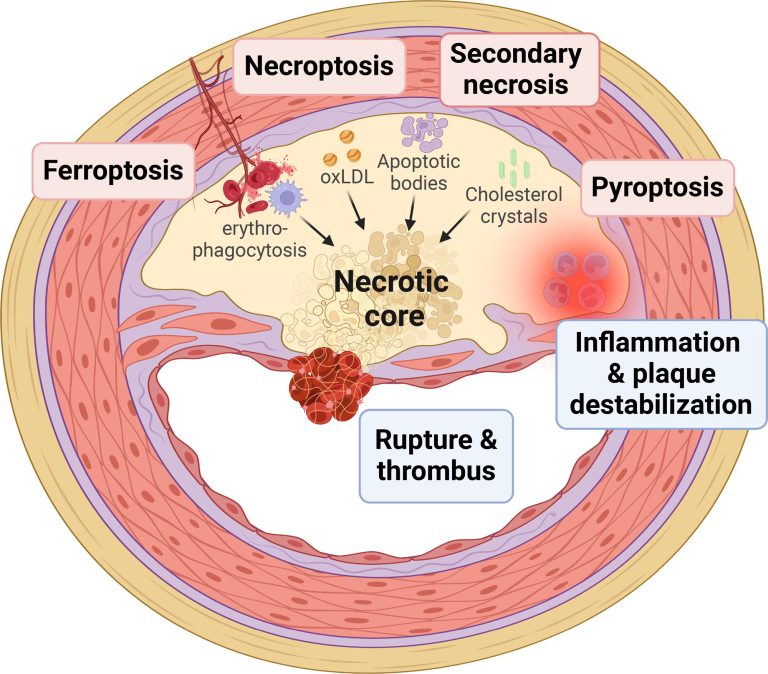
1. Cardiovascular disease: High blood sugar levels can damage the blood vessels and increase the risk of cardiovascular disease.
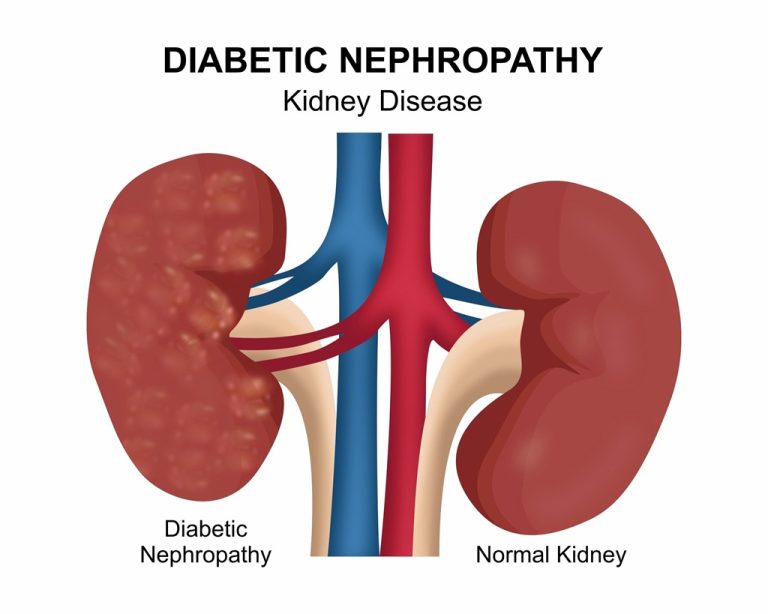
2. Kidney damage: High blood sugar levels can damage the kidneys and increase the risk of kidney failure.
3. Nerve damage: High blood sugar levels can damage the nerves and increase the risk of nerve damage.
4. Blindness: High blood sugar levels can damage the blood vessels in the eyes and increase the risk of blindness.
5. Amputation: High blood sugar levels can damage the nerves and blood vessels in the feet and increase the risk of amputation.
Conclusion
Type 2 diabetes is a chronic metabolic disorder that requires careful management and treatment to prevent complications. By understanding the causes, symptoms, diagnosis, treatment,