Type 1 Diabetes: A Comprehensive Guide
Type 1 diabetes is a chronic autoimmune disease in which the body’s immune system attacks and destroys the cells in the pancreas that produce insulin, a hormone that regulates blood sugar levels. This results in a complete deficiency of insulin production, requiring individuals with type 1 diabetes to rely on insulin therapy to control their blood sugar levels. In this article, we will discuss the causes, symptoms, diagnosis, treatment, and management of type 1 diabetes.

Causes of Type 1 Diabetes
The exact causes of type 1 diabetes are still not fully understood, but research suggests that it is a complex interplay of genetic and environmental factors. Some of the known risk factors for developing type 1 diabetes include:
1. Genetics: Having a family history of type 1 diabetes increases the risk of developing the disease.
2. Autoimmune disorders: Individuals with a history of other autoimmune disorders, such as thyroid disease or celiac disease, are at increased risk of developing type 1 diabetes.
3. Environmental factors: Exposure to certain environmental toxins, such as viruses or chemicals, may trigger the autoimmune response that leads to type 1 diabetes.
Symptoms of Type 1 Diabetes
The symptoms of type 1 diabetes can develop rapidly, often over a few weeks. Some of the common symptoms include:
1. Increased thirst and urination: High blood sugar levels can cause the body to produce more urine, leading to dehydration and increased thirst.
2. Fatigue: High blood sugar levels can cause fatigue, weakness, and a general feeling of being unwell.
3. Weight loss: Despite increased appetite, individuals with type 1 diabetes may experience weight loss due to the body’s inability to use glucose for energy.
4. Blurred vision: High blood sugar levels can cause the lens in the eye to swell, leading to blurred vision.
5. Slow healing of cuts and wounds: High blood sugar levels can impair the body’s ability to heal wounds and cuts.
Diagnosis of Type 1 Diabetes
The diagnosis of type 1 diabetes is typically made based on a combination of clinical symptoms, physical examination, and laboratory tests. Some of the common diagnostic tests used to diagnose type 1 diabetes include:
1. Fasting blood glucose test: This test measures the level of glucose in the blood after an overnight fast.
2. Oral glucose tolerance test: This test measures the level of glucose in the blood after consuming a sugary drink.
3. Autoantibody tests: These tests measure the presence of autoantibodies in the blood, which can indicate an autoimmune response.
4. Insulin and C-peptide tests: These tests measure the level of insulin and C-peptide in the blood, which can indicate the presence of type 1 diabetes.
Treatment and Management of Type 1 Diabetes
The treatment and management of type 1 diabetes typically involves a combination of insulin therapy, lifestyle modifications, and regular monitoring of blood sugar levels. Some of the common treatment options for type 1 diabetes include:
1. Insulin therapy: Insulin is typically administered via injection or an insulin pump, and is used to regulate blood sugar levels.
2. Carbohydrate counting: This involves tracking the amount of carbohydrates consumed and adjusting insulin doses accordingly.
3. Blood glucose monitoring: Regular monitoring of blood sugar levels is essential to ensure that levels remain within a healthy range.
4. Lifestyle modifications: Maintaining a healthy diet, engaging in regular physical activity, and managing stress can all help to manage type 1 diabetes.
Complications of Type 1 Diabetes
If left unmanaged, type 1 diabetes can lead to a range of complications, including:
1. Diabetic ketoacidosis: A life-threatening condition that occurs when the body produces high levels of ketones.
2. Hypoglycemia: A condition that occurs when blood sugar levels drop too low.
3. Nerve damage: High blood sugar levels can damage the nerves, leading to numbness, tingling, and pain.
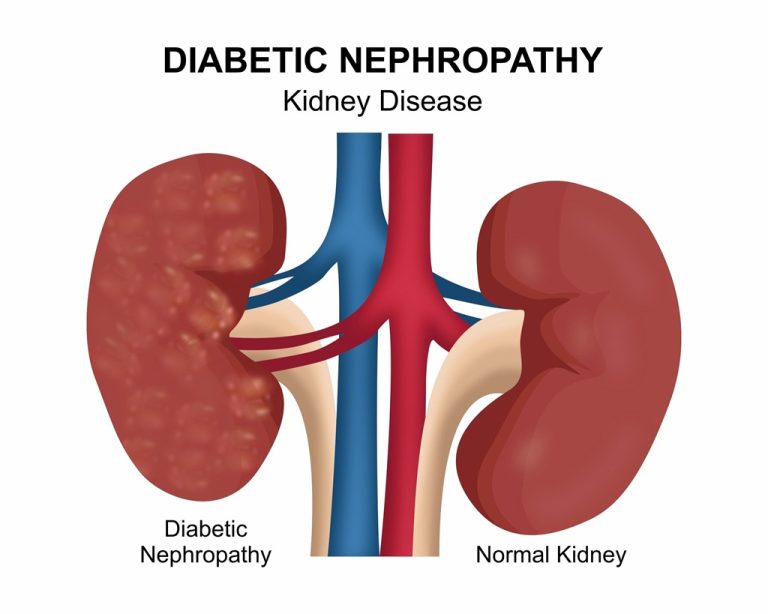
4. Kidney damage: High blood sugar levels can damage the kidneys, leading to kidney failure.
5. Blindness: High blood sugar levels can damage the blood vessels in the eyes, leading to blindness.
Conclusion
Type 1 diabetes is a chronic autoimmune disease that requires careful management and treatment to prevent complications. By understanding the causes, symptoms, diagnosis, treatment, and management of type 1 diabetes, individuals can take control of their condition and live a long and healthy life.