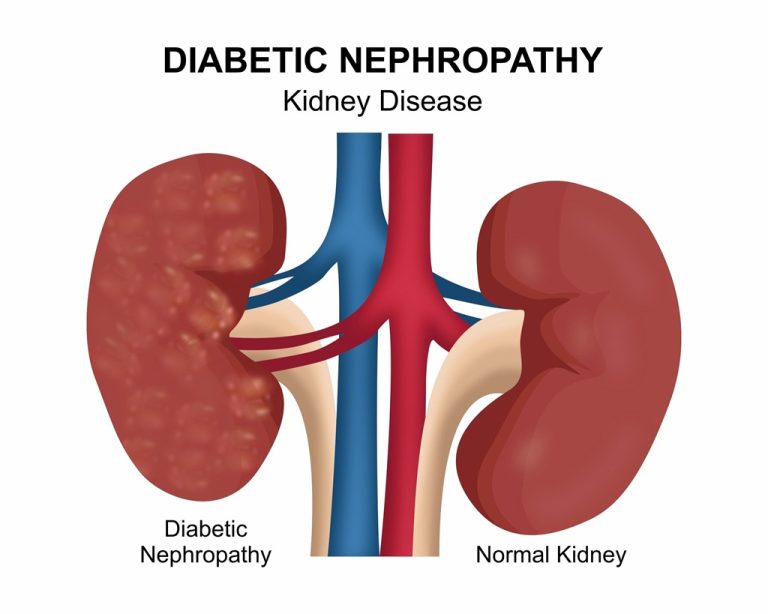
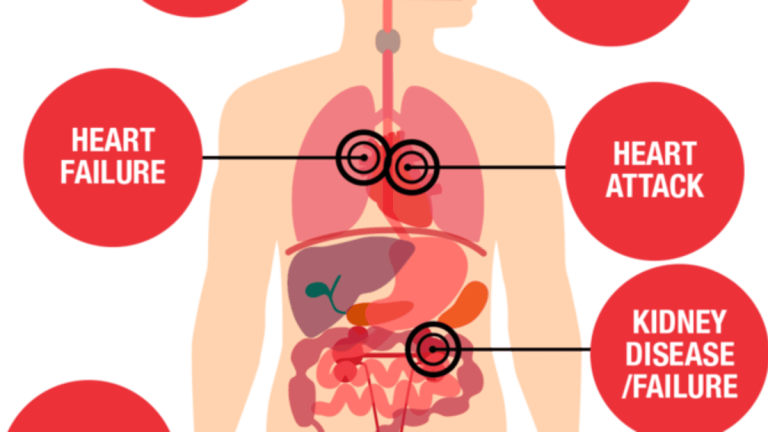
Atherosclerosis is a medical condition characterised by the buildup of plaque in the arteries, leading to their hardening and narrowing.
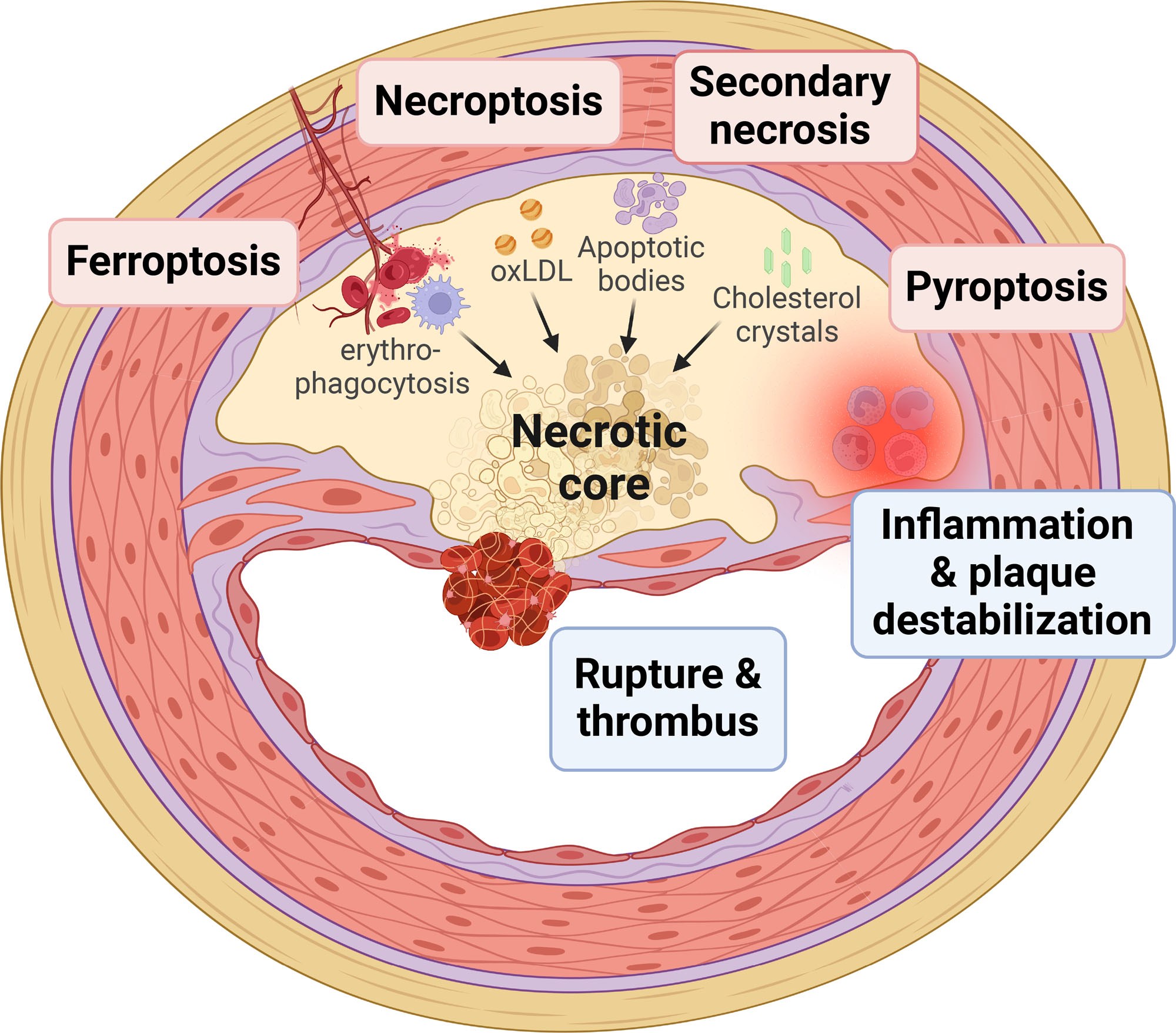
This process can restrict blood flow to vital organs, including the heart, brain, and kidneys, increasing the risk of cardiovascular disease. Atherosclerosis is a leading cause of death and disability worldwide, accounting for over 17 million deaths annually.
Causes of Atherosclerosis
Atherosclerosis is a complex condition, and its causes are multifactorial. Some of the main causes include:
1. _High Blood Pressure_: Hypertension can damage the inner lining of the arteries, making them more susceptible to plaque buildup.
2. _High Cholesterol_: Elevated levels of low-density lipoprotein (LDL) cholesterol can contribute to plaque formation.
3. _Smoking_: Tobacco smoke can damage the inner lining of the arteries, increasing the risk of atherosclerosis.
4. _Diabetes_: High blood sugar levels can damage the arteries, making them more susceptible to plaque buildup.
5. _Obesity_: Excess weight can increase the risk of developing atherosclerosis.
6. _Physical Inactivity_: A sedentary lifestyle can contribute to the development of atherosclerosis.
7. _Family History_: A family history of atherosclerosis or cardiovascular disease can increase an individual’s risk.
8. _Age_: Atherosclerosis is a degenerative condition, and the risk increases with age.
_Symptoms of Atherosclerosis_
Atherosclerosis can be asymptomatic for many years, and symptoms may only appear when the condition has advanced. Some common symptoms include:
1. _Chest Pain_: Angina or chest pain can occur when the heart muscle does not receive enough oxygen-rich blood.
2. _Shortness of Breath_: Shortness of breath, or dyspnoea, can occur when the heart is unable to pump enough blood to meet the body’s needs.
3. _Pain or Weakness in the Legs_: Pain or weakness in the legs can occur when the arteries in the legs become narrowed or blocked.
4. _Dizziness or Lightheadedness_: Dizziness or lightheadedness can occur when the brain does not receive enough oxygen-rich blood.
5. _Confusion or Disorientation_: Confusion or disorientation can occur when the brain does not receive enough oxygen-rich blood.
_Diagnosis of Atherosclerosis_
Diagnosing atherosclerosis typically involves a combination of physical examination, medical history, and diagnostic tests. Some common diagnostic tests include:
1. _Angiography_: Angiography uses X-rays and a contrast agent to create detailed images of the blood vessels.
2. _Ultrasound_: Ultrasound uses high-frequency sound waves to create images of the blood vessels.
3. _Computed Tomography (CT) Scan_: A CT scan uses X-rays to create detailed images of the blood vessels.
4. _Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI)_: An MRI uses magnetic fields and radio waves to create detailed images of the blood vessels.
5. _Blood Tests_: Blood tests can measure lipid profiles, blood sugar levels, and other markers of cardiovascular disease.
_Treatment of Atherosclerosis_
Treatment for atherosclerosis typically involves a combination of lifestyle changes and medications. Some common lifestyle changes include:
1. _Dietary Changes_: Eating a healthy diet that is low in saturated fats, cholesterol, and sodium can help to reduce the risk of atherosclerosis.
2. _Regular Exercise_: Regular physical activity can help to improve cardiovascular health and reduce the risk of atherosclerosis.
3. _Weight Loss_: Losing weight can help to reduce the risk of atherosclerosis.
4. _Stress Reduction_: Reducing stress through techniques such as meditation, yoga, and deep breathing exercises can help to reduce the risk of atherosclerosis.
Some common medications used to treat atherosclerosis include:
1. _Statins_: Statins are cholesterol-lowering medications that can help to reduce the risk of atherosclerosis.
2. _Beta Blockers_: Beta blockers can help to slow the heart rate and reduce blood pressure.
3. _Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme (ACE) Inhibitors_: ACE inhibitors can help to lower blood pressure and reduce the risk of atherosclerosis.
4. _Aspirin_: Aspirin can help to prevent blood clots from forming and reduce the risk of atherosclerosis.
_Prevention of Atherosclerosis_
Preventing atherosclerosis requires making healthy lifestyle choices and managing risk factors. Some common prevention strategies include:
- 1. _Maintaining a Healthy Weight_: Maintaining a healthy weight can help to reduce the risk of atherosclerosis.
2. _Eating a Healthy Diet_: Eating a healthy diet that is low in saturated fats, cholesterol, and sodium can help to reduce the risk of atherosclerosis.
3. _Regular Exercise_: Regular physical activity can help to improve cardiovascular health and reduce the risk of atherosclerosis.4. _Not Smoking_: Not smoking can help to reduce the risk of atherosclerosis.
5. _Managing Stress_: Managing stress through techniques such as meditation, yoga, and deep breathing exercises can help to reduce the risk of atherosclerosis.

Atherosclerosis: A Comprehensive Review Other stories
-
Hypertension: A Silent Killer
-
Atherosclerosis: A Leading Cause of Cardiovascular Disease
-
Causes and Risk Factors of Diabetes
-
Pulmonary Function Test: A Comprehensive Guide
-
Allergy Testing: A Comprehensive Guide for Asthma Sufferers