Diabetic Nephropathy: Causes, Symptoms, and Treatment Options
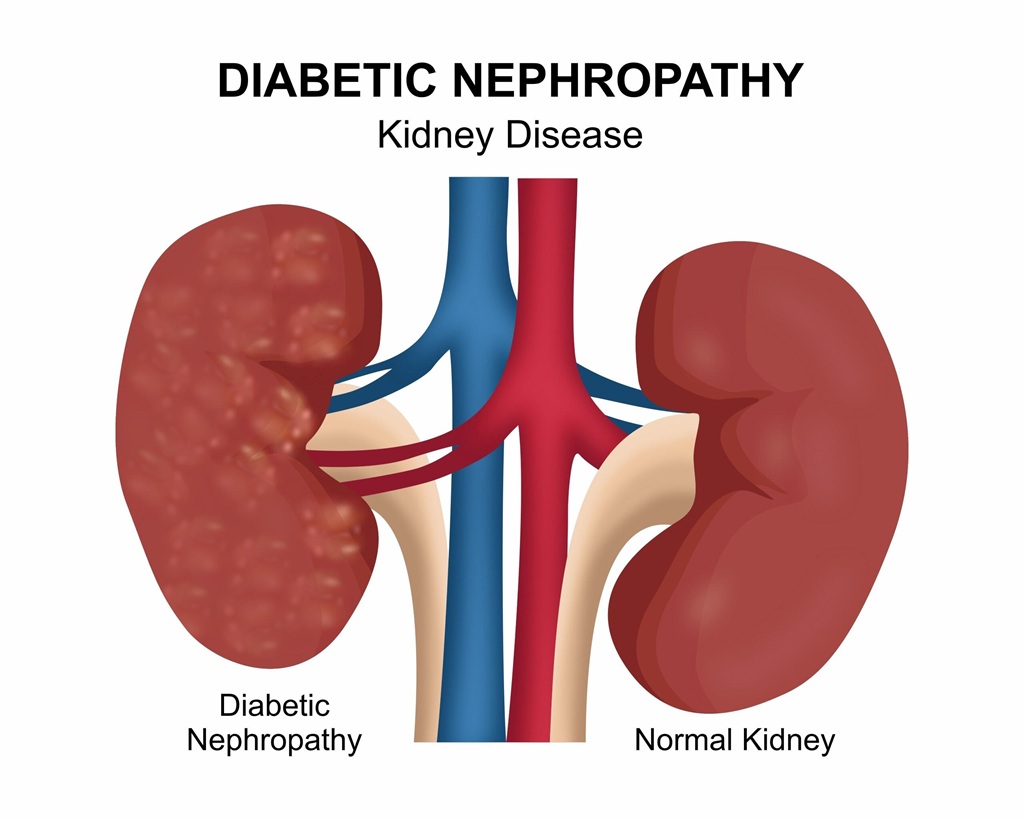
Diabetic nephropathy, also known as diabetic kidney disease, is a serious complication of diabetes that can lead to kidney failure and even death. It is a leading cause of chronic kidney disease and end-stage renal disease worldwide. In this article, we will discuss the causes, symptoms, and treatment options for diabetic nephropathy.

Causes of Diabetic Nephropathy
Diabetic nephropathy is caused by damage to the kidneys’ tiny blood vessels, which are responsible for filtering waste and excess fluids from the blood. High blood sugar levels can damage these blood vessels, leading to:
1. _Microalbuminuria_: The presence of small amounts of albumin (a protein) in the urine, which is an early sign of kidney damage.
2. _Proteinuria_: The presence of large amounts of protein in the urine, which can lead to kidney failure.
3. _Glomerulosclerosis_: Scarring of the glomeruli, the tiny blood vessels in the kidneys that filter waste and excess fluids from the blood.
4. _Tubulointerstitial Fibrosis_: Scarring of the tubules and interstitium, the tissues that surround the glomeruli and help filter waste and excess fluids from the blood.
_Symptoms of Diabetic Nephropathy_
The symptoms of diabetic nephropathy can vary depending on the severity of the disease. In the early stages, there may be no symptoms at all. As the disease progresses, symptoms can include:
1. _Swelling_: Swelling in the legs, ankles, and feet due to fluid retention.
2. _Fatigue_: Feeling tired and weak due to the buildup of toxins in the blood.
3. _Nausea and Vomiting_: Nausea and vomiting due to the buildup of toxins in the blood.
4. _Itching_: Itching due to the buildup of toxins in the blood.
5. _Muscle Cramps_: Muscle cramps due to electrolyte imbalances.
_Risk Factors for Diabetic Nephropathy_
Several risk factors can increase the likelihood of developing diabetic nephropathy, including:
1. _Duration of Diabetes_: The longer a person has diabetes, the higher their risk of developing diabetic nephropathy.
2. _Blood Sugar Control_: Poor blood sugar control can increase the risk of diabetic nephropathy.
3. _Hypertension_: High blood pressure can increase the risk of diabetic nephropathy.
4. _High Cholesterol_: High cholesterol levels can increase the risk of diabetic nephropathy.
5. _Smoking_: Smoking can increase the risk of diabetic nephropathy.
_Treatment Options for Diabetic Nephropathy_
Treatment for diabetic nephropathy depends on the severity of the disease. In the early stages, treatment may focus on managing blood sugar levels, blood pressure, and cholesterol levels. In more advanced cases, treatment may include:
1. _Medications_: Medications such as angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitors and angiotensin receptor blockers (ARBs) can help slow the progression of diabetic nephropathy.
2. _Dialysis_: Dialysis may be necessary for individuals with end-stage renal disease.
3. _Kidney Transplantation_: Kidney transplantation may be necessary for individuals with end-stage renal disease.
4. _Lifestyle Changes_: Lifestyle changes such as following a healthy diet, exercising regularly, and quitting smoking can help manage blood sugar levels, blood pressure, and cholesterol levels.
_Prevention of Diabetic Nephropathy_
Preventing diabetic nephropathy requires careful management of blood sugar levels, blood pressure, and cholesterol levels. Additionally, regular check-ups with a healthcare provider can help detect diabetic nephropathy in its early stages, when it is more treatable. Other prevention strategies include:
1. _Maintaining a Healthy Diet_: Eating a healthy, balanced diet that is low in sugar, salt, and unhealthy fats can help manage blood sugar levels and reduce the risk of diabetic nephropathy.
2. _Exercising Regularly_: Regular exercise can help manage blood sugar levels and reduce the risk of diabetic nephropathy.
3. _Quitting Smoking_: Quitting smoking can reduce the risk of diabetic nephropathy and other complications of diabetes.
4. _Managing Stress_: Managing stress through techniques such as meditation and yoga can help reduce the risk of diabetic nephropathy.