Diabetic retinopathy is a serious complication of diabetes that can lead to blindness if left untreated. It is a leading cause of vision loss in adults, affecting over 4 million people worldwide. In this article, we will discuss the causes, symptoms, and treatment options for diabetic retinopathy.
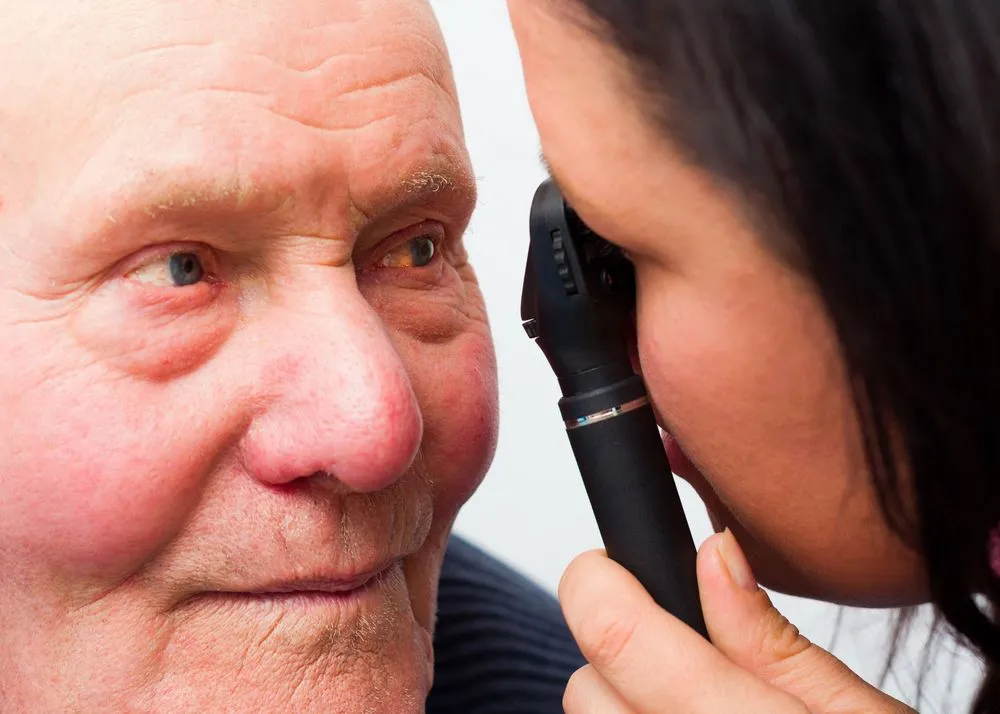

Causes of Diabetic Retinopathy
Diabetic retinopathy is caused by damage to the blood vessels in the retina, which is the light-sensitive tissue at the back of the eye. High blood sugar levels can damage the blood vessels, causing them to leak or become blocked. This can lead to a range of problems, including:
1. _Microaneurysms_: Small swellings in the blood vessels that can leak fluid and cause vision problems.
2. _Retinal Haemorrhages_: Bleeding in the retina that can cause vision loss.
3. _Hard Exudates_: Deposits of fat and protein that can accumulate in the retina and cause vision problems.
4. _Macular Oedema_: Swelling in the macula, the part of the retina responsible for central vision.
_Symptoms of Diabetic Retinopathy_
The symptoms of diabetic retinopathy can vary depending on the severity of the condition. In the early stages, there may be no symptoms at all. As the condition progresses, symptoms can include:
1. _Blurred Vision_: Blurred vision or double vision can occur due to damage to the blood vessels in the retina.
2. _Floaters_: Small, dark spots that appear to float in front of the eyes can be a symptom of diabetic retinopathy.
3. _Flashes of Light_: Flashes of light or sudden changes in vision can occur due to damage to the blood vessels in the retina.
4. _Vision Loss_: In severe cases, diabetic retinopathy can cause vision loss or even blindness.
_Risk Factors for Diabetic Retinopathy_
Several risk factors can increase the likelihood of developing diabetic retinopathy, including:
1. _Duration of Diabetes_: The longer a person has diabetes, the higher their risk of developing diabetic retinopathy.
2. _Blood Sugar Control_: Poor blood sugar control can increase the risk of diabetic retinopathy.
3. _Hypertension_: High blood pressure can increase the risk of diabetic retinopathy.
4. _High Cholesterol_: High cholesterol levels can increase the risk of diabetic retinopathy.
5. _Smoking_: Smoking can increase the risk of diabetic retinopathy.
_Treatment Options for Diabetic Retinopathy_
Treatment for diabetic retinopathy depends on the severity of the condition. In the early stages, treatment may focus on managing blood sugar levels and reducing blood pressure and cholesterol levels. In more advanced cases, treatment may include:
1. _Laser Surgery_: Laser surgery can be used to reduce swelling in the retina and prevent further vision loss.
2. _Anti-VEGF Injections_: Anti-VEGF injections can be used to reduce swelling in the retina and prevent further vision loss.
3. _Vitrectomy_: Vitrectomy is a surgical procedure that involves removing the vitreous gel from the eye to reduce swelling and prevent further vision loss.
4. _Retinal Detachment Surgery_: Retinal detachment surgery is a surgical procedure that involves reattaching the retina to the back of the eye.
_Prevention of Diabetic Retinopathy_
Preventing diabetic retinopathy requires careful management of blood sugar levels, blood pressure, and cholesterol levels. Additionally, regular eye exams can help detect diabetic retinopathy in its early stages, when it is more treatable. Other prevention strategies include:
1. _Maintaining a Healthy Diet_: Eating a healthy, balanced diet that is low in sugar, salt, and unhealthy fats can help manage blood sugar levels and reduce the risk of diabetic retinopathy.
2. _Exercising Regularly_: Regular exercise can help manage blood sugar levels and reduce the risk of diabetic retinopathy.
3. _Quitting Smoking_: Quitting smoking can reduce the risk of diabetic retinopathy and other complications of diabetes.
4. _Managing Stress_: Managing stress through techniques such as meditation and yoga can help reduce the risk of diabetic retinopathy.