Atherosclerosis: A Leading Cause of Cardiovascular Disease
Atherosclerosis is a complex and multifactorial disease that affects millions of people worldwide. It is a leading cause of cardiovascular disease, stroke, and death.

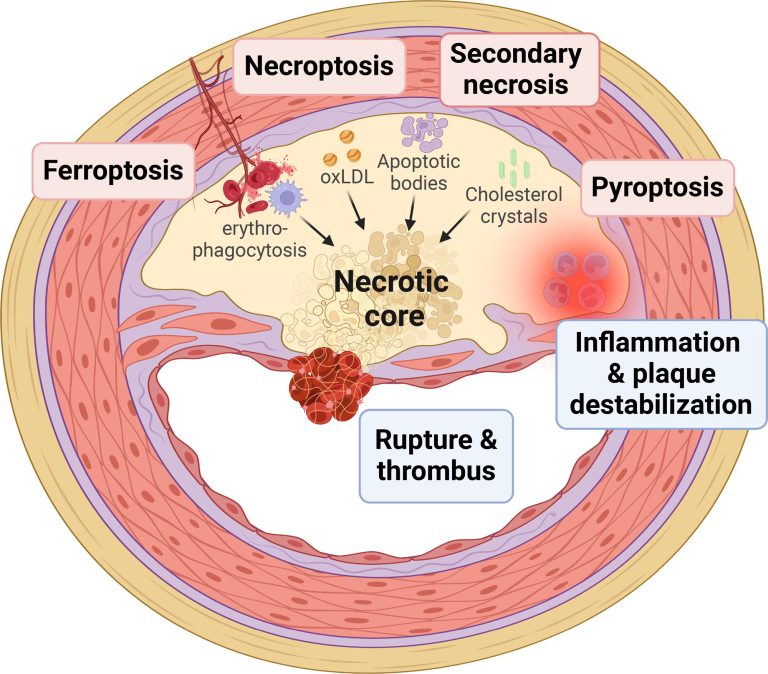
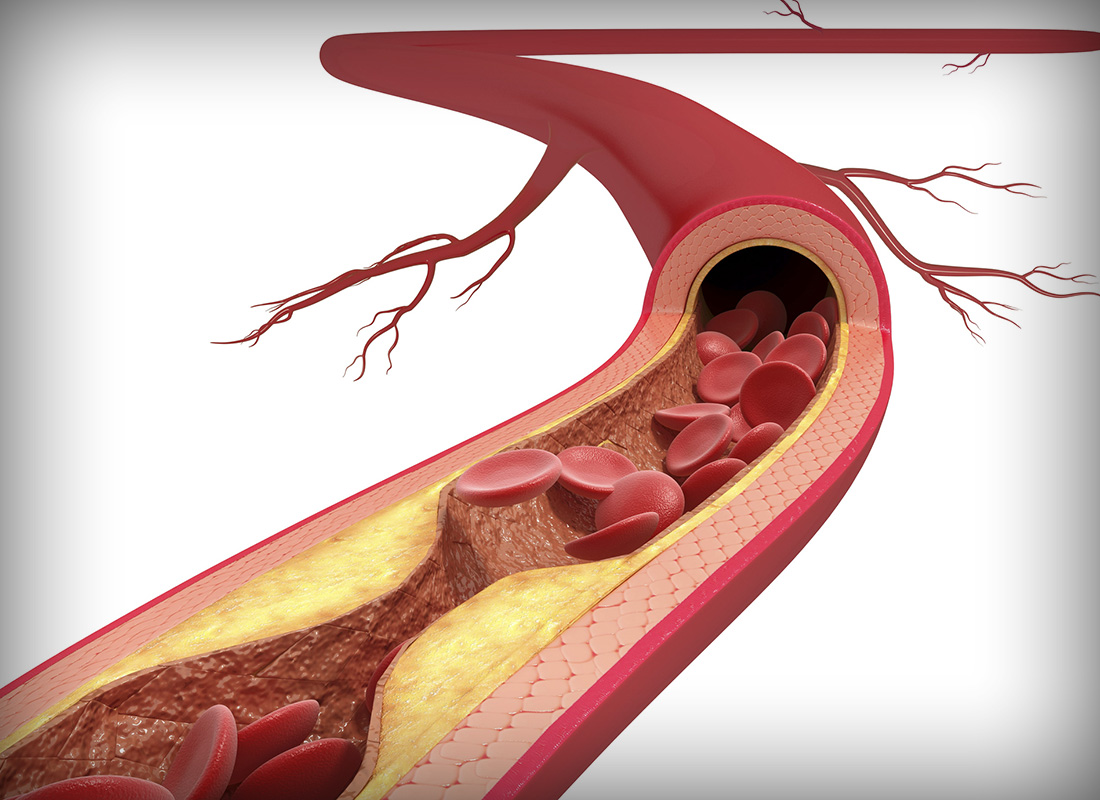
The disease is characterised by the buildup of plaque in the arteries, leading to their hardening and narrowing. This process can restrict blood flow to vital organs, including the heart, brain, and kidneys.
While atherosclerosis is a serious disease, it is also preventable and treatable. By making healthy lifestyle choices, such as eating a healthy diet, exercising regularly, and not smoking, individuals can reduce their risk of developing atherosclerosis. Additionally, medications such as statins, beta blockers, and ACE inhibitors can help to slow the progression of the disease and reduce the risk of cardiovascular events.
Early detection and treatment of atherosclerosis are critical to preventing long-term damage and reducing the risk of cardiovascular events. Healthcare providers can use a variety of diagnostic tests, including angiography, ultrasound, and CT scans, to diagnose atherosclerosis and monitor its progression.
In conclusion, atherosclerosis is a serious and complex disease that requires a comprehensive approach to prevention and treatment. By making healthy lifestyle choices, managing risk factors, and seeking early detection and treatment, individuals can reduce their risk of developing atherosclerosis and its associated cardiovascular events.
References
1. World Health Organisation. (2017). Cardiovascular diseases.
2. American Heart Association. (2017). Atherosclerosis.
3. National Institutes of Health. (2019). Atherosclerosis.
4. Mayo Clinic. (2020). Atherosclerosis.
5. Centres for Disease Control and Prevention. (2020). Atherosclerosis.
Future Directions
While significant progress has been made in understanding and managing atherosclerosis, there is still much to be learned. Future research directions may include:
1. Personalised Medicine: Developing personalised treatment approaches based on an individual’s unique genetic and environmental profile.
2. Imaging Techniques: Improving imaging techniques to better diagnose and monitor atherosclerosis.
3. Novel Therapies: Developing new therapies, such as gene therapy and cell-based therapies, to treat atherosclerosis.
4. Lifestyle Interventions: Investigating the impact of lifestyle interventions, such as diet and exercise, on atherosclerosis prevention and treatment.
5. Health Disparities: Examining the impact of health disparities on atherosclerosis risk and outcomes.